But Rashays co-founder Rami Ykmour, who made headlines during Covid for clashing with police over masks and speaking out against banning unvaccinated diners, says labor shortages – not the floods – are to blame for rising prices.
“I am disgusted, I am really disappointed with what’s going on out there, guys,” the outspoken restaurateur said in a TikTok video.
“Listen to this. We are buying a box of lettuce for $140. How much are we going to pass on to our customers? How can we pass on that expense to our customer? Even the big fast food giants have stopped serving their magic burger because this is worth, what, seven, eight bucks? One head of lettuce?
Mr Ykmour said he “can’t believe this”.
“Guys, just to get lettuce out to our restaurant is costing us so much money there is no way customers will come back if we pass on that cost,” he said, adding beef prices had also “gone through the roof”.
“And you know what they tell us? Let’s blame the floods. You know what I call that? BS,” he said.
“Do you know what the real problem is? The real problem is we’re short labour. The real problem is no one is out there to pick cos lettuce, there’s no one out there to pick iceberg. There’s no one to work in our farms, there’s no one to work in our country abattoirs. That’s why the prices have gone up, but they’re covering up for it.”
He said it was “time the government stepped in and said listen, we’re going to open the gates, we’re going to let people here and we’re going to make it easy for small business to run their business, we’ re going to let people come into the country and work here”.
“Guys, this is getting ridiculous,” he said. “Now ask for something to be done.”
Speaking to news.com.au on Friday, Mr Ykmour insisted labor shortages were responsible for price increases in production.
“I can tell you that first-hand,” he said.
“I was on a lettuce farm in Melbourne last week, they had six people on and usually they have 40 people. [The floods] did contribute in the early days, but it’s got nothing to do with what’s happening today.”
Mr Ykmour said governments needed to once again incentivize people to come to Australia to work, with something similar to the “Ten Pound Poms” scheme after World War II.
“We’re at that level now,” he said.
He said he believed border closures over the past two years had “of course” caused labor shortages, but that the issue was much broader.
“I think people just don’t want to work,” he said. “Coming off the pandemic, people are struggling.”
Recruiters have previously warned Australia is grappling with a massive skills shortage as employers struggle to fill roles.
Graham Wynn from Superior People Recruitment told news.com.au in June that he had “never seen it this bad”.
“This is the worst and most difficult it’s been to find people,” he said, adding it was “across the board”.
“Salespeople, technicians, a bit of IT we’re struggling with as well, but even the more basic roles which don’t require any experience like receptionists, we’re even struggling to find those at the moment.”
Mr Ykmour agreed, saying his business was getting hit with a “double-whammy” as a result.
“It’s [affecting] the price of produce, and we’re getting hit with staff shortages, right from the top level all the way down to waiters,” he said.
“My head office employs 60 people and we’re struggling, it’s just permanent recruitment. What used to take four weeks to find you’re now looking at three months.”
I have argued lockdowns were partly to blame for the general malaise, along with Covid itself.
“I think we’ve trained people to stay at home with lockdowns and all the rest,” he said.
“We’ve told people, listen, it’s OK to stay at home. I reckon a lot of people in the community are mentally drained on the back of the pandemic — people are finding it hard to just survive at the moment.”
Prime Minister Anthony Albanese is coming under increased pressure from the states and the business lobby to ramp up immigration to address lingering skills shortages after two years of Covid border closures.
Last year, NSW government bureaucrats urged Premier Dominic Perrottet to push the federal government for an “explosive” post-WWII-style immigration surge that could bring in two million people over five years.
NSW Skills Minister Alister Henskens last month called on the Albanese government to implement a “significant acceleration” of the nation’s skilled migration program, Australian reported.
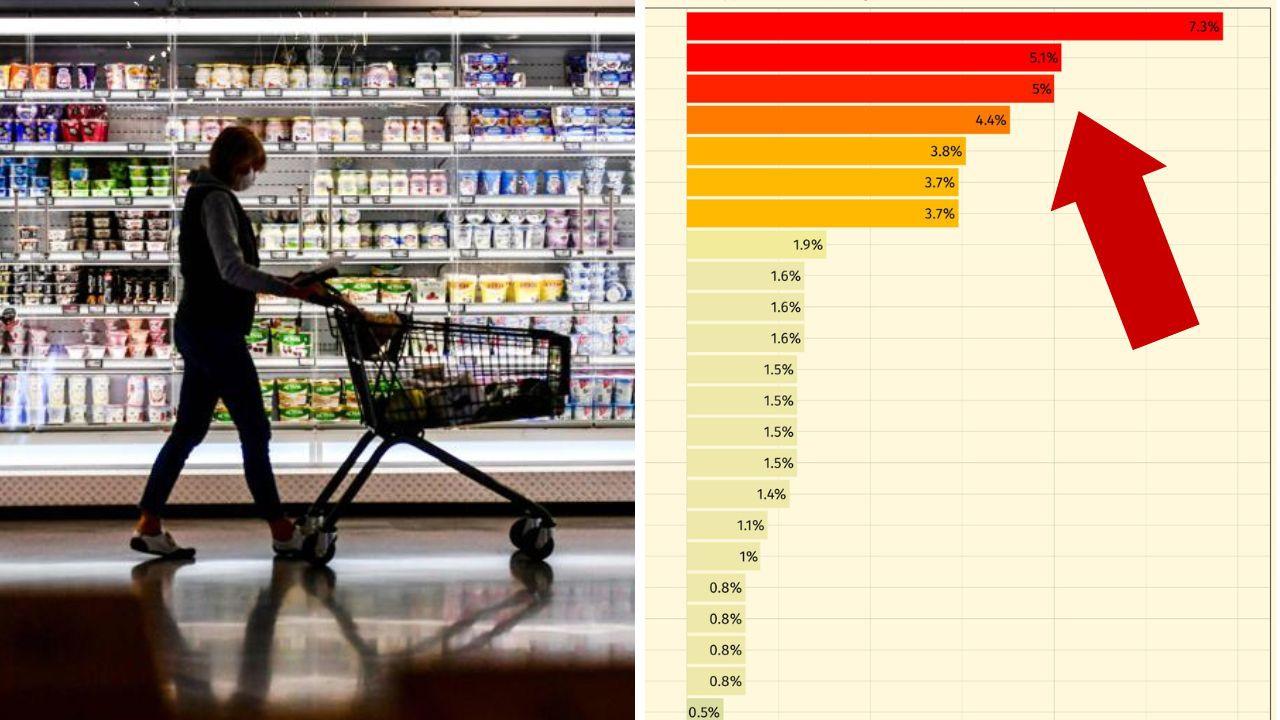
Australia’s annual inflation rate rose to 6.1 per cent in the June quarter, figures released last week show, the fastest pace since December 1990.
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, the most significant contributors to the 1.8 rise in consumer prices over the quarter were new dwelling purchases, automotive fuel and furniture.
Price rises were also seen across all food and non-food grocery products, “reflecting a range of price pressures including supply chain disruptions and increased transport and input costs”, the ABS said.
Fruit and vegetable prices were up 7.3 per cent compared with the same quarter last year, meat and seafood rose 6.3 per cent, bread and cereal products were also up 6.3 per cent, while dairy and related products increased by 5.2 per cent.
“Fruit and vegetables rose 5.8 per cent [in the June quarter] due to heavy rainfall and flooding in key production areas of NSW and Queensland disrupting domestic supply,” the ABS said.
“Covid – related supply chain disruptions and high transport and fertilizer costs also contributed to the rise. Bread and cereal products rose 3.1 per cent due to constrained global wheat supply.”
The ABS noted meals out and takeaway foods also rose 1.4 per cent “due to rising input costs and ongoing supply and labor shortages”.
“Dining vouchers offered by the NSW and Victorian governments and the Melbourne City Council partially offset the rise,” it said.
“These voucher schemes have the effect of reducing out-of-pocket costs for consumers. Excluding the impact of these voucher schemes, Meals out and takeaway foods rose 2.1 per cent.”
[email protected]
Read related topics:sydney
.